Video: Pirates or Coastguards?

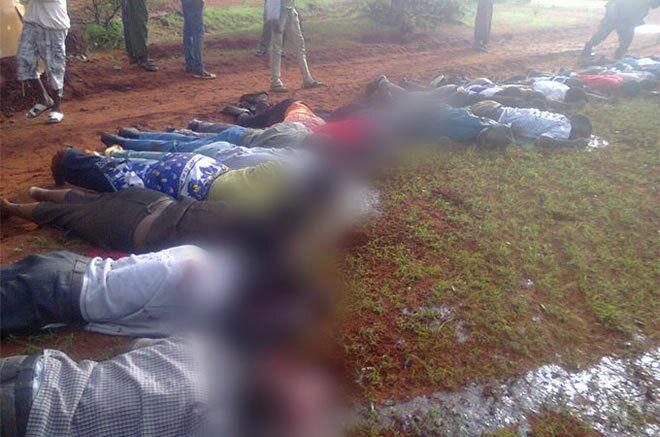
Somali sources close to the trade say that the dumped materials included radioactive uranium, lead, cadmium, mercury and industrial, hospital, chemical and various other toxic wastes. In 1992, Unep said that European firms were involved in the trade, but because of the high level of insecurity in the country there were never any accurate assessments of the extent of the problem.
Why has piracy become a major problem in the Gulf of Aden and the Indian Ocean? Some say it’s a response to the turmoil Somalia has been going through.
WATCH THE PROGRAM HERE (Presented by CBC)
In 1997 and 1998, the Italian newspaper Famiglia Cristiana, which jointly investigated the allegations with the Italian branch of Greenpeace, published a series of articles detailing the extent of illegal dumping by a Swiss firm, Achair Partners, and an Italian waste broker, Progresso.
The European Green Party followed up the revelations by presenting to the press and the European Parliament in Strasbourg copies of contracts signed by the two companies and representatives of the then “President†— Ali Mahdi Mohamed — to accept 10 million tonnes of toxic waste in exchange for $80 million (then about £60 million).
Abdullahi Elmi Mohamed, a Somali academic studying in Sweden, told The Times that this worked out at “approximately $8 per tonne, while in Europe the cost for disposal and treatment of toxic waste material could go up to $1,000 per tonneâ€.
“Times online”WATCH THE PROGRAM HERE (Presented by CBC)
Comments
comments
 Calendar
Calendar