In 2013, possibilities for stability from Somalia to South China Sea
 Policymakers in many of the world’s hot spots have a common New Year’s wish: for unity to usher in and consolidate political and economic stability.
Policymakers in many of the world’s hot spots have a common New Year’s wish: for unity to usher in and consolidate political and economic stability.
The international news of any year is a disparate affair, a global chronicle of courage, calamity, and close calls. The interconnectedness of events is not always clear.
But looking ahead to 2013, whether in Syria, South America, or the South China Sea, policymakers have a common New Year’s wish: for unity to usher in and consolidate political and economic stability.
Europe turns toward integration
After another year in the depths of a debt crisis that has tested the viability of the European Union, leaders made a major step forward at the end of the year: agreeing to give the European Central Bank oversight of the biggest banks in the Union.
Recommended: How well do you know global Christmas traditions? Take the quiz
Skeptics dismiss the agreement as a watered-down initiative of common-denominator compromises and delays. But it paves the way for an eventual banking union, and caps off a year of expressed commitments to deeper integration.
“The decision of European heads of state to create a banking union and a fiscal union still needs to be implemented. But that was a genuine game changer in a sense,” says Jan Techau, director of Carnegie Europe at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace in Brussels. “It is by no means perfect and is not seen in action yet; but if this comes, that will create momentum for more political integration.”
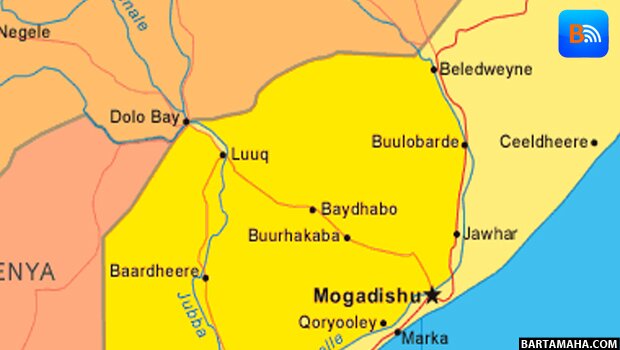
In Africa, a new dawn for Somalia?
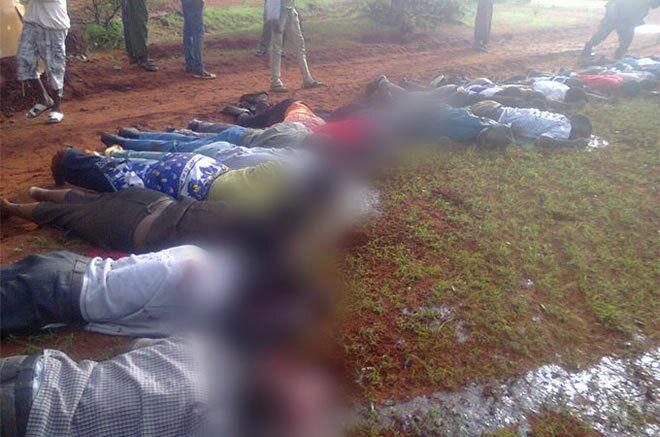
In Somalia, Al Qaeda was on the run in 2012 after four years in control of the country’s south, pushed out of all of its major urban strongholds by African Union military offensives.
Get our FREE 2013 Global Security Forecast now
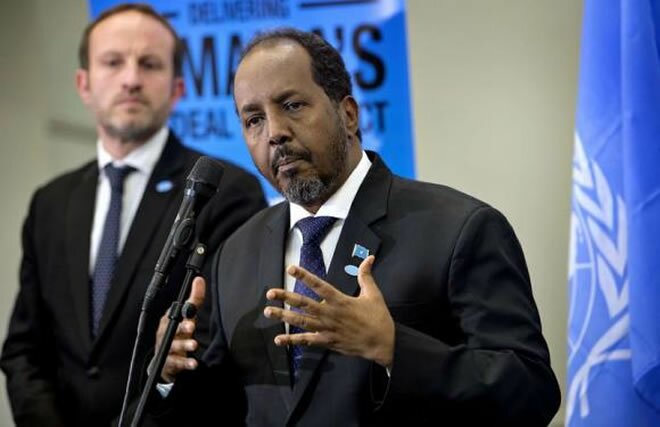
Somalia’s Western allies – also its financiers – have begun proclaiming a new dawn. International commercial flights now land regularly at Mogadishu’s refurbished airport. Investors from the large Somali diaspora are returning home. Aid workers have ever-greater access to the millions of people still in grave need.
But analysts are wary. A large number of rank-and-file fighters may have deserted Al Shabab, but hard-line commanders remain. Many of them, trained in Pakistan with Al Qaeda, are regrouping in Somalia’s north.
“The Somali government is going to need very quickly to show that it brings dividends, health, education, road repairs, to the population, or they may well turn back to supporting Shabab,” one Western diplomat focused on Somalia says in an e-mail. “There is a very narrow window to prove the government is the better option. Probably less than nine months. The early part of 2013 will be crucial.”
Meanwhile, across the continent in Mali, events moved in the opposite direction in 2012. An ethnic Taureg rebellion spiraled into a takeover of the north by Islamist militants, while the army ousted Mali’s democratically elected president. Malians hope that in 2013 their country can reunite and that democracy will be restored. If not, Western and African leaders fear Mali could become a failed state.
Some Malians say only force can dislodge the Islamists, while others place hope in dialogue. Meanwhile, worry is growing that ethnic grudges might transform a possible intervention into a tragedy of unintended consequences.
“Families affected by crisis may seek vengeance,” says Mohamed Ag Ossad, the director of Tumast, a Tuareg cultural center in Bamako. “The state should take things in hand before there’s an ethnic war.”
This month soldiers loyal to coup leader Captain Amadou Sanogo removed Mali’s interim prime minister – a brazen show of force that the US said endangered national dialogue and delayed a government recapture of the north, according to a statement on Dec. 11. Members of the security forces are also accused of beating, detaining, and killing critics of the army, as well as Tuareg and Arab men, said a December 20 report by Human Rights Watch.
For Moussa Mara, an accountant and district mayor in Bamako, such problems underline the need to reestablish democratic rule by holding presidential elections that were derailed by this year’s coup. “Crisis can be an opportunity for our country,” he says. “If we’re intelligent.”
Middle East: to the victors, more divisions?
As pressure has mounted against Syria’s embattled president, Bashar al-Assad, many are starting to ask what will come of the opposition Free Syrian Army should the regime fall.
A number of Syria experts warn that without a plan to disarm opposition groups, they risk destabilizing the country.
“What do you do with the men with guns? The men who don’t have jobs…. We’ve seen this in Libya, and we also saw it in Iraq,” says Aram Nerguizian, a Syria expert at the Center for Strategic and International Studies.
The vast majority of Free Syrian Army units in Syria say they will put down their weapons and let democracy determine their future after Mr. Assad. Still, a number of observers worry that there is a possibility armed groups may want an undue stake in Syria’s government, and the challenge for 2013 will be to incorporate them into civilian life.
In Israel and the Palestinian territories, positions on both sides hardened as the window for a two-state solution rapidly closed. Israel moved further to the right heading into January elections, while Palestinians became more assertive with a perceived victory against Israel in the November Gaza conflict and an overwhelming vote recognizing Palestine as a state at the United Nations.
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu has repeatedly invited the Palestinians to return to the negotiating table without preconditions at any time and indicated that the Palestinians’ failure to do so shows they are not serious about peace. But Palestinians say they cannot afford to negotiate while Israel steadily expands settlements in the West Bank. Nearly 10 percent of Israeli Jews now live over the 1967 borders, which the recent UN resolution recognized as the basis for a future Palestinian state.
In 2013, Palestinians want to see an end to settlement expansion before it is too late to implement a two-state solution. “We are witnessing today a very crucial moment … a moment of irreversibility,” says Mustapha Barghouthi, a former Palestinian presidential candidate and democracy activist.
Israelis, for their part, seek Palestinian recognition of Israel as a Jewish state, as well as assurances that a peace deal will mark the end to the conflict and not merely a stepping stone to regaining all of historic Palestine.
East Asia’s symbiotic ties
In a year when China made several neighbors nervous over its territorial claims, Beijing’s most alarming spat was with Japan over a handful of uninhabited islands known in China as the Diaoyu and in Japan as the Senkaku. Although a war over the issue is highly unlikely, it has come to be seen as not altogether impossible, as tensions have risen in recent months.
But it is the economic fallout already under way that analysts say the two must address immediately. “China is Japan’s biggest market, and Japan is a very important source for China to learn new science and technology,” says Zhou Weihong, a Japan expert at Beijing Foreign Studies University. If the second-largest economy in the world [China] and the third-largest [Japan] are not getting along, “that is bad news for the rest of the world,” Professor Zhou says. “There are big enough motives for both sides to want to improve their relationship.”
The reach of Chávez
The biggest story of 2012 in Venezuela was the reelection of President Hugo Chávez in October, despite significant gains made by the opposition. But now, facing illness, Mr. Chávez might not be able to stand for his Jan. 10 inauguration – and may have to step down.
Venezuela is holding its breath – as is the region that sees Chávez as a beacon of the left, some of whose members, like Cuba, depend heavily on his largess. Within the oil-rich country, political tensions will flare in 2013 until a new leader is selected, while daily problems such as crime and inflation mount, says Caracas-based political analyst Jose Vicente Carrasquero. “Over time, we will adjust under a new government,” he says, “and surely after this process of transition we will discover a new way of doing politics in Venezuela, something that we need.”
* Also contributing: staff writers Peter Ford in Beijing and Christa Case Bryant in Jerusalem; correspondents John Thorne in Mali, Tom Peter in Aleppo, Syria, and Mike Pflanz in Somalia.
Source:- CS Monitor
Comments
comments
 Calendar
Calendar